What is GNSS vulnerability?
Highly valuable, all too vulnerable
Consider the speed of today’s financial markets. Think about air traffic control systems, military or healthcare infrastructure. All now rely on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). GNSS comprises GPS (operated by the USA), GLONASS (Russia), BEIDOU (China) and Galileo (Europe), with satellites constantly transmitting precise location and timing data to millions of connected devices. Recently, the airspace around Tel Aviv International airport fell victim to what is known as a spoofing attack, with planes displaying incorrect data to pilots, resulting in disruption and the potential for multiple serious incidents. GNSS signals are also regularly jammed. So-called jamming attacks occur when satellite signals are blocked so that no data can reach receivers in the affected area. And then there are equally dangerous threats from space weather. Activity on the sun can cause disturbances in Earth’s ionosphere leading to minor yet significant deviations in timing accuracy at the receiver end.
Building resilience
GNSS provides highly accurate location and timing data for key infrastructure – but it cannot be relied on alone.
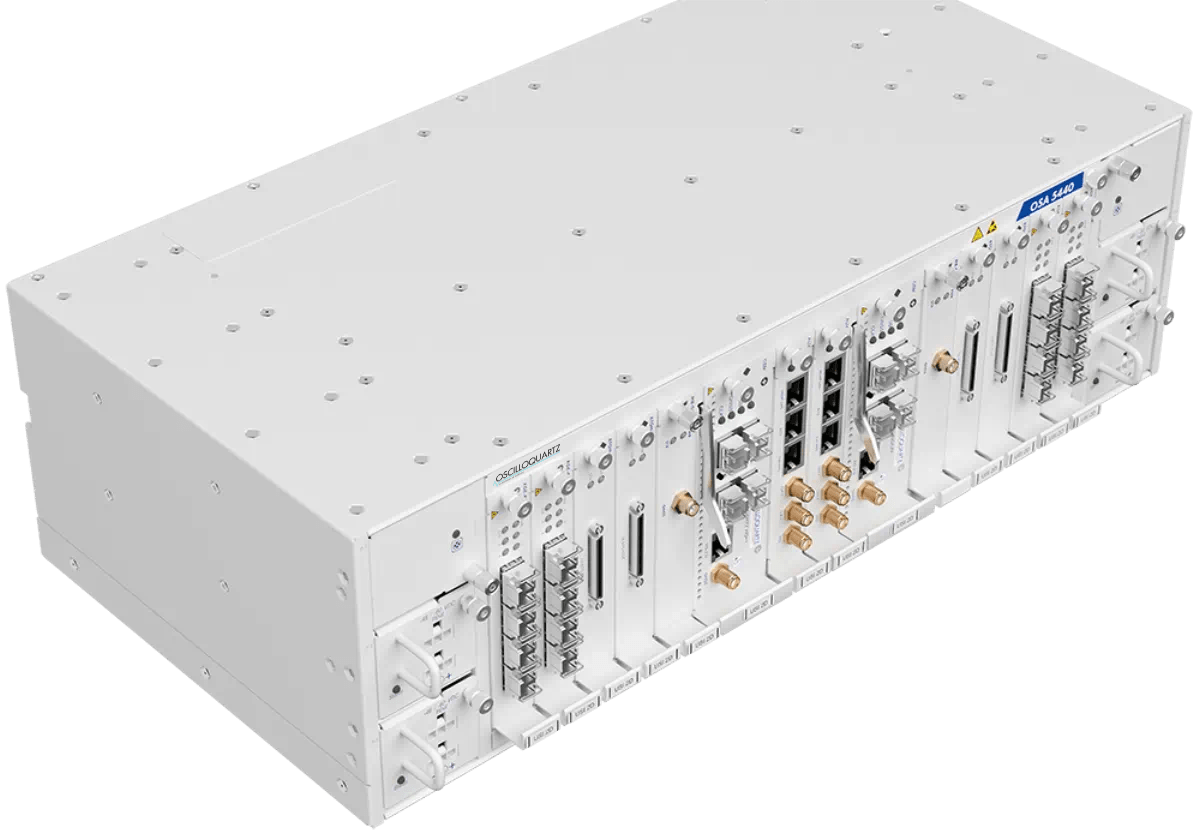
Adtran's Oscilloquartz timing solutions are designed to compensate for GNSS vulnerabilities, providing assured and highly accurate timing, even in the event of a prolonged outage.
Multi-band protection
Multi-band GNSS receivers offer resilience to jamming and spoofing attacks. They can also determine and then compensate for ionospheric delay variations.
Whatever the (space) weather
Communications service providers (CSPs) are reliant on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) sourced from GNSS to keep today’s high-speed data networks in sync. But when GNSS becomes unreliable due to deliberate interference or an errant solar flare, what then? Fortunately, options exist designed to combat these threats. Multi-band antennas have access to more satellites and a wider spectrum. In a world of increasing jamming and spoofing attacks, this gives receivers a far better chance of retrieving accurate information from GNSS signals. Multi-band technology can also compensate for timing aberrations caused by space weather. And, in the event of a total loss of GNSS data, enhanced primary reference time clocks (ePRTCs) are now recommended. Designed to distribute precise timing information, ePRTCs can remain within 100nsec of UTC for a minimum of 14 days.
AI-powered analytics
Adtran SatAware™ is the easiest and most efficient way for operators to remotely monitor and correct for GNSS vulnerabilities at multiple receiver sites.

The complete GNSS protection toolkit
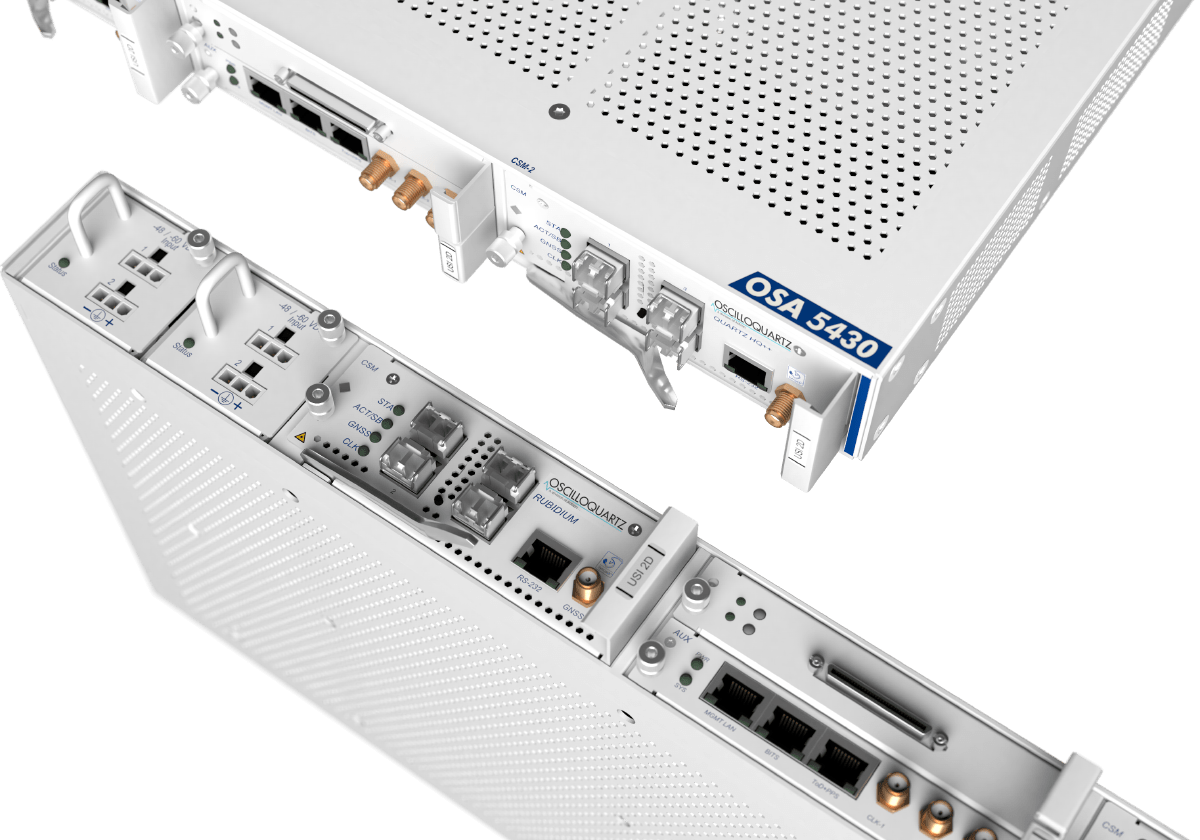
Our advanced timing solutions are designed to compensate for GNSS vulnerabilities, providing assured and highly accurate timing, even in the event of a prolonged outage. Our fully redundant and highly scalable ePRTC solutions combine GNSS grandmasters with a high-quality atomic cesium clock to deliver incredibly accurate timing for a minimum of 14 days – a giant leap for holdover capacity. We also offer our SatAware™ system, a remote monitoring platform for GNSS management. Operators using its groundbreaking AI-based analytics can monitor and correct for GNSS issues without the need to visit remote sites. What’s more, our multi-band GNSS receiver is also available as a pluggable line card that can be partnered with our OSA 5430 or OSA 5440 to enhance jamming and spoofing detection, increase availability and compensate for signal delays caused by space weather.
